Osteochondritis Dissecans
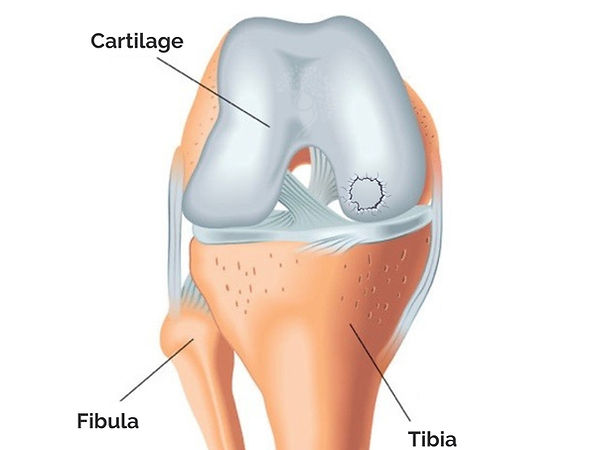
Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is a condition that affects the knee joint, especially in children, adolescents, and young adults. It is a lesion behind the cartilage, known as the subchondral bone. Osteochondritis can compromise the cartilage lining the joint, causing pain, swelling, and, in some cases, locking of the knee.
If left untreated, OCD can progress to early osteoarthritis. Therefore, it is important to recognize the signs and seek appropriate treatment.
What causes osteochondritis dissecans?
There is still no single defined cause, but there are some theories in which the main related factors are:
-
Repetitive microtraumas to the knee, such as during sports activities;
-
Blood supply problems in the subchondral bone;
-
Genetic and constitutional factors.
The most frequently affected area is the inner part of the medial femoral condyle.
Symptoms
Symptoms of osteochondritis dissecans can vary greatly depending on the stage of the injury and include:
-
Knee pain, especially after physical activity;
-
Swelling (joint effusion);
-
Popping or crackling sensation;
-
Episodes of joint locking, when fragments are loose within the joint;
-
Decreased muscle strength, especially in the quadriceps.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis begins with a thorough discussion with the patient to understand the characteristics of the symptoms and when the pain occurs. A proper clinical evaluation, including a thorough physical examination of the knee, is also crucial. Specific tests such as the Wilson maneuver can help identify the disease. This test reproduces the pain experienced when internally rotating the tibia during knee extension from 90% flexion. The pain is relieved by external rotation.
Confirmation of osteochondritis dissecans and assessment of severity are performed using imaging tests:
-
X-rays from different angles;
-
MRI, which is the primary test for assessing the severity of the injury, cartilage viability, and bone fragment stability;
-
Arthroscopy, which allows direct visualization of the injury.

Types of osteochondritis dissecans
OCD is classified into two types:
-
Juvenile (JCOD): occurs in patients with active bone growth. It has a greater chance of healing with conservative treatment.
-
Adult (ADOC): appears after the growth plate closes. It usually has a worse prognosis.
Treatment
Treatment depends on age, injury stability, and the presence of loose fragments within the joint.
Conservative Treatment
Most recommended for young patients with stable injuries.
May include:
-
Reduced physical activity;
-
Use of crutches to relieve weight on the knee;
-
Physical therapy and muscle strengthening;
-
Monitoring with imaging tests.
Surgical Treatment
Indicated in cases of failure of conservative treatment, unstable injuries or injuries with loose fragments, and injuries in adults with a lower chance of spontaneous healing.
Techniques vary depending on the type of injury:
-
Subchondral bone drilling: stimulates natural healing;
-
Fragment fixation with screws or pins: to keep the fragment viable in place;
-
Microfractures: small perforations to stimulate local bleeding and the formation of fibrocartilage, with or without a collagen membrane covering the injury;
-
Autologous osteochondral transplant (mosaicplasty): uses cartilage and bone cylinders harvested from another area of the knee;
-
Autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI): cells from the patient's own cartilage are cultivated and reimplanted;
-
Osteochondral allograft: transplant of cartilage and bone from a donor, reserved for more severe cases.
Final Considerations
Young patients with small, stable lesions have an excellent prognosis with conservative treatment. In advanced cases or in adults, the risk of progression to osteoarthritis is higher, especially if treatment is delayed or inadequate.
Osteochondritis dissecans of the knee is a serious condition, but it can be successfully treated, especially when diagnosed early. Children and adolescents who play sports should be alert to persistent knee pain. Follow-up with a specialized orthopedic surgeon is essential to ensure the best outcome.

